The Australian business landscape witnesses predictable trends in buyer demand, affecting business sales throughout the year. To assist Australian businesses, this analysis explores the cyclical patterns of buyer interest and their implications for sellers and business brokers. These patterns, identified over more than two decades, have a significant impact on the timing, pricing, and success of business transactions.
A comprehensive examination of buyer demand has revealed consistent fluctuations in monthly rates of buyer enquiries. Several months stand out as the busiest periods when potential buyers express the highest interest in acquiring businesses. These months are Jan – March, September to November. April, May, June, July, and December also tend to be quieter.
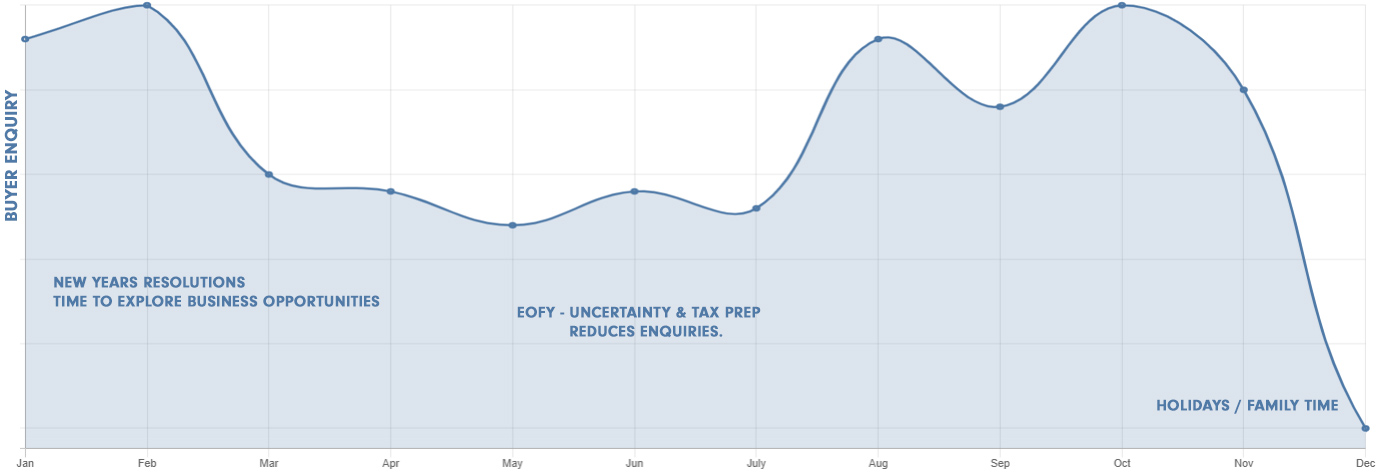
Several factors contribute to the annual fluctuations in buyer demand for businesses in Australia. Understanding the drivers behind these patterns is essential for businesses and brokers to make informed decisions. Here are some reasons why these fluctuations exist:
Seasonal Trends
Seasonal variations in buyer demand can be linked to holidays and special events. For instance, January and early December tend to be busy months as many people have time off work and are in a more relaxed state of mind, making it an opportune time for them to explore business opportunities.
In summary, a combination of economic, seasonal, and personal factors, along with marketing strategies and local influences, drive the fluctuations in buyer demand for businesses in Australia. Business owners and brokers can leverage this knowledge to optimize their selling and buying strategies and achieve better outcomes in the dynamic business sales market.
It is important to note that there are regional variations in buyer demand. For instance, Queensland experiences a rapid increase in demand from the early days of January, whereas Adelaide and Melbourne have a slower buildup. Additionally, special events, such as football finals and the Bathurst weekend, contribute to lower buyer interest. Similarly, Melbourne witnesses a lull in the last week of October and the first week of November, attributed to the Spring Racing carnivals and Melbourne Cup.
The annual ebb and flow of buyer demand underscore the significance of timing when selling a business to achieve the best asking price. The correlation between demand and price is undeniable. Selling a business when demand is on the rise, such as in January, generally results in a higher selling price and a faster transaction. Conversely, attempting to sell in the quieter months of June, July, or August may lead to a slower sale process, often requiring price reductions and yielding less favourable outcomes.
Therefore, business owners are encouraged to align their selling strategies with the peaks in buyer demand. Analysing buyer demand data and planning sales accordingly can significantly enhance the outcome of business transactions. Read more tips for a successful business sale .

In addition to timing, business sellers in Australia should be familiar with the concept of EBITDA add backs. EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) add backs are expenses or deductions that are added back to the EBITDA figure to reflect the true earning potential of the business. These add backs are important for business sellers as they can positively impact the business's perceived value.
Example Formula for EBITDA Add Back Calculation
EBITDA is a popular method to calculate the asking price for a business. To calculate EBITDA add backs, sellers should identify and quantify expenses that are not essential to the core operations of the business. An example formula for EBITDA add back calculation is as follows:
EBITDA Add Back = Non-Recurring Expenses + Owner's Perks + One-Time Costs
By adding back non-recurring expenses, owner's perks, and one-time costs to the EBITDA, sellers can present a more accurate picture of the business's profitability to potential buyers, potentially increasing the perceived value of the business.

In conclusion, Australian businesses can benefit from understanding the annual buyer demand cycles. Timing business sales to coincide with peaks in buyer demand can lead to higher sale prices and faster transactions. Additionally, the concept of EBITDA add backs is a valuable tool for business sellers, helping to present a more accurate view of the business's financial performance to prospective buyers. In this dynamic market, preparation and strategic planning are key for both business owners and business brokers to maximize their success in the sales process.